Europe and the United States share the same Western culture with similar values such as representative democracy, separation of powers and respect for the law. However, there are important differences, one of which is the absence of a universal health care system in the USA. Although, from a European point of view, this may seem difficult to understand, the truth is that a simple review of American history helps to understand why there is no national health system in that country.
Why doesn’t the United States have universal public health care?
- Cultural differences: The USA was born as a nation of immigrants with an enterprising spirit who, from the east coast went westward, fighting with nature and native tribes. Thus, an individualism that is still very present in society was fostered. One of the consequences of individualism is distrust in authority and, therefore, in government.
- Private insurers: the country has a significant number of insurance companies that do not share the idea of a public healthcare system. According to Reuters, in 2019 the US healthcare industry invested $30 billion in marketing.

- American Medical Association (AMA): has historically opposed a national public health care system.
- World War II: after the conflict (1939-1945) Europe was destroyed and bankrupt, while the U.S. economy became the largest in the world. The precarious situation in Europe led governments to support public health care, which was not considered necessary in the wealthy American society.
- Inertia: human beings are generally opposed to change. In order to establish a national health service in the USA, it would be necessary to overcome a multitude of barriers, ranging from legislation to customs and practices.
10 notes on the U.S. health care system:
- In 1965, two government health insurance programs were introduced: Medicare (especially for people over 65 years of age) and Medicaid (mainly for people of limited means).
- In 2010, under President Barack Obama, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was implemented, bringing health insurance to more people, although the system has its fair share of detractors.
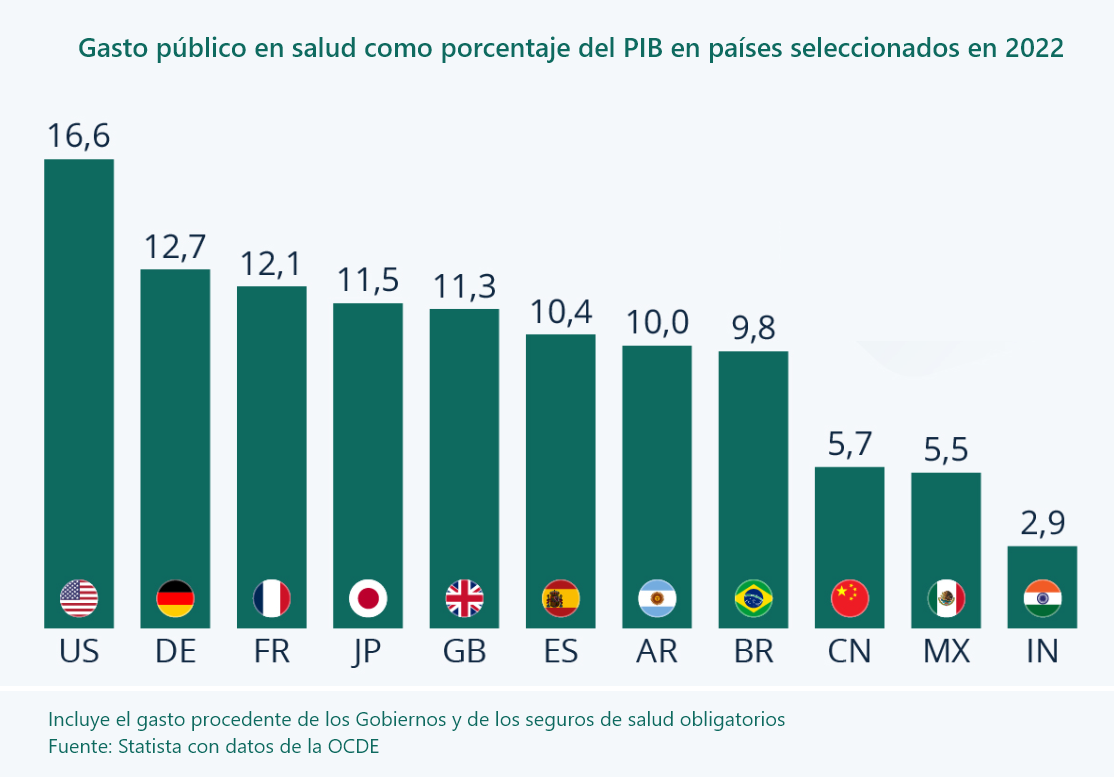
- The United States spends about 17% of GDP on healthcare, more than any other advanced country.
- The healthcare market is valued at around 1.3 trillion euros.
- The U.S. population is 340 million, of which some 27 million lack any type of health insurance.
- Fifty-four percent of the population has health insurance through the company where they work, although in this case the worker often has to pay a portion.
- OECD data show that the tax-to-GDP ratio is much higher in the EU than in the US, partly because Europe has to finance universal health care.
- The cost of healthcare in the USA is more expensive than in Europe: doctor’s visits, hospitalizations, medicines and treatments.
- The U.S. method, being basically private, tends to have shorter waiting times than in Europe.
- The United States is a world leader in medical research and tends to adopt new treatments more quickly than in Europe. For example, it leads in fields such as cancer treatment, heart surgery and organ transplantation. Most of the vaccines and treatments for, for example, combating AIDS or Covid were born in U.S. laboratories